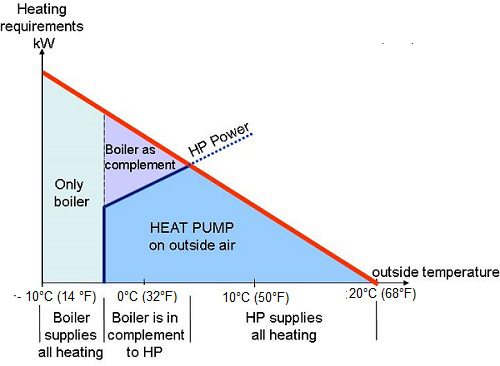
Heat pumps on exterior air water training
There are exterior air heat pump models:
- With the evaporator fitted outside (like the condenser of an air conditioner)
- With the evaporator fitted inside the building (see photo below). In this case, the outside air passes through an intake and discharge duct. To avoid condensation of the duct in winter, it is thermally insulated.

As much as possible, Air ext – Water HP must be coupled to low temperature heating systems because:
- Heat pump performance degrades as the heating water temperature increases.
- Most HP cannot produce DHW at more than 55 [°C] (131 °F) (however there are models today, called « high temperature » capable of producing water at 65 [°C] (149 °F) and higher, but with more or less reduced coefficients of performance.
In
renovation,
Air ext – Water HP are, in general, installed to
contribute to
heating, without being capable (or sufficiently sized) of satisfying
all requirements (see course « Performance & Installation
of Heat Pumps »).
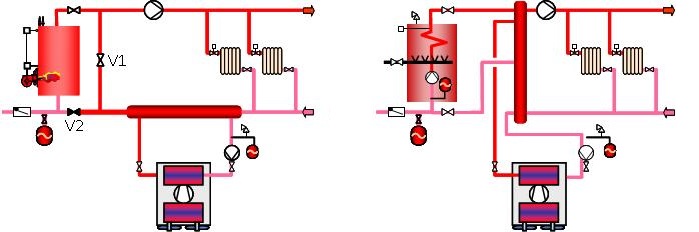
The
heating season can therefore be broken up into periods in which:
- The HP supplies all the heating (season end).
- The boiler ensures the complement of the HP (mid-season).
- The heat pump stops when the water return temperature is too high (extreme cold).