We can identify (see course : « Condensing boilers »):
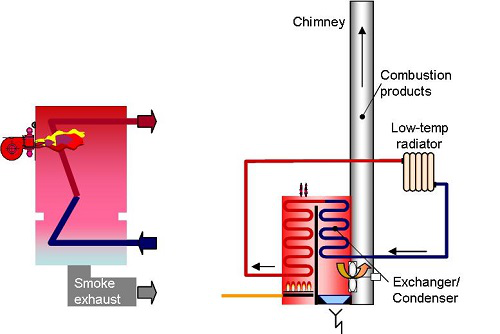
- Single return condensing boilers (called « 2 connection »)
In these boilers the exchanger is totally or partly manufactured from rust-proof materials. Low power boilers, like wall-mounted gas-fired condensing boilers, belong to this category.
A
2 connection boiler
- Double return condensing boilers (called « 3 connection »)
These boilers are designed to allow the separation of heating returns, subject to temperature. The lower temperature returns flow through the part of the boiler at the smoke exhaust. This allows a maximum cooling of combustion gases and thus favours condensation.
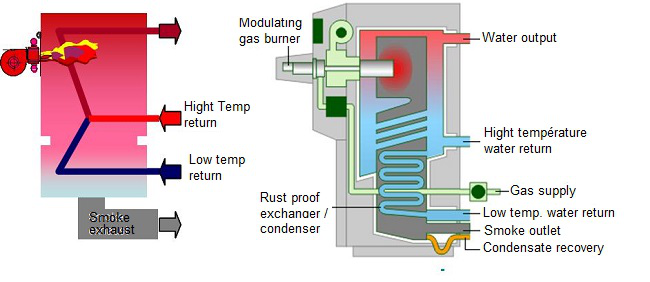
A 3 connection boiler Source Guillot
- Separate condenser boilers (called « 4 connection »)
It is completely feasible to design a « condensing boiler » composed of a standard boiler and a supplementary exchanger (condenser) which is installed on the gas exhaust conduit. We can also call the condenser a “recuperator”.
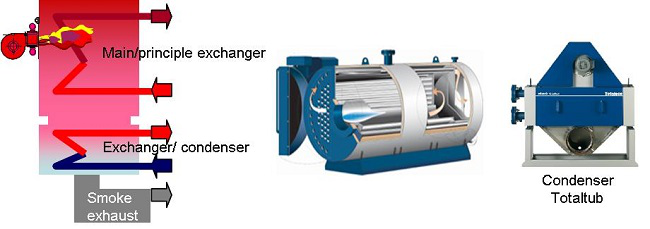
4
connection boiler
Standard boiler & condenser/recuperator
Whatever the type, condensing boiler efficiency increases with the drop in temperature of the condenser through flow.
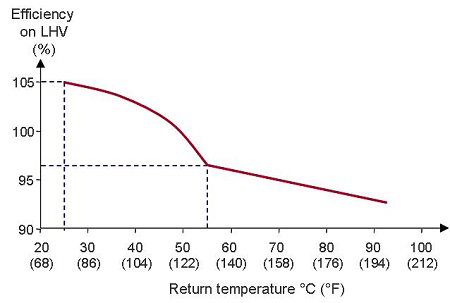
For natural gas condensing boilers, condensation takes place at through flow temperatures of < 55 [°C] (131 °F).
The present course deals with connecting single and double return condensing boilers in heating systems without domestic hot water production.
