Air
handling units (AHU) allow the control, by temperature and at times
by hygrometry, of the quality of delivered air.
The units are
composed of pre-made elements and assemblies in an air supply casing
and at times in an air intake casing.

Air handling units are mainly used:
- To treat fresh ventilation air to be delivered to buildings.
We
talk of air handlers or “100%
fresh air handlers”.
The
delivered air flow to air buildings is approx. 20 to 30 [m3/h]
(700 to 1050 ft3/h)
and per person.
Normally,
a fresh air ventilation unit does not deal with heating. It only
handles the heating up (and eventually cooling down) of fresh air, to
change from outside temperature to ambient temperature.
The blown
fresh air is therefore neutral from a temperature angle (it delivers
neither heating nor cooling) in relation to the treated rooms.
With
this kind of unit, heating and air conditioning of rooms is therefore
handled by another system, treating heat losses (off ventilation) and
eventually air conditioning loads. This could be a radiator circuit
or a FCU.
- To handle the ventilation and the heating (and eventually the cooling) of rooms.
Usually, the flow just for building ventilation is in general too low to permit heating (and possibly cooling). Complementing fresh air, the unit recycles exhaust air from the treated rooms. The unit is no longer “100% fresh air”.
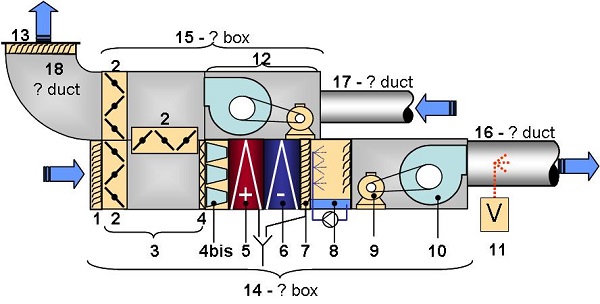
An air handling unit can be made up of:
Question
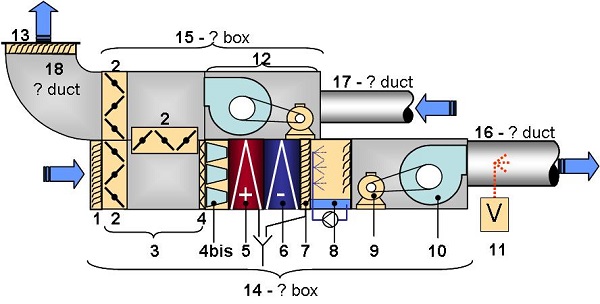
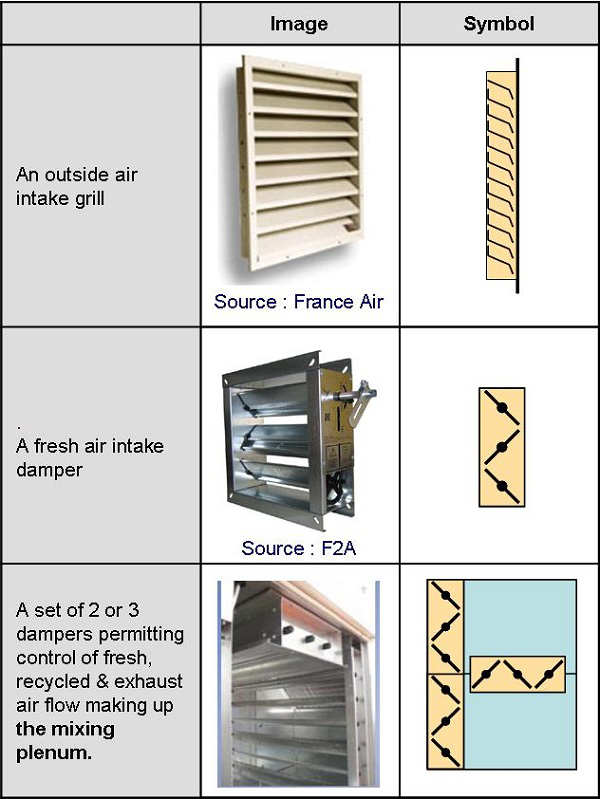
1: Fresh air intake grill
2: Dampers
3: Mixing plenum
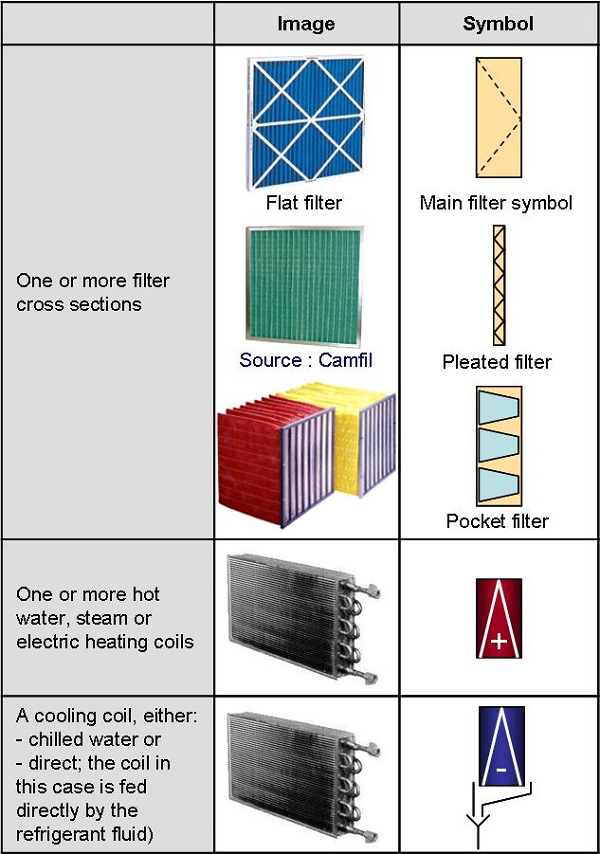
4: 1st filter row, pleated filter
4 b: 2nd filter row, pocket filter
5: Heating coil
6: Cooling coil
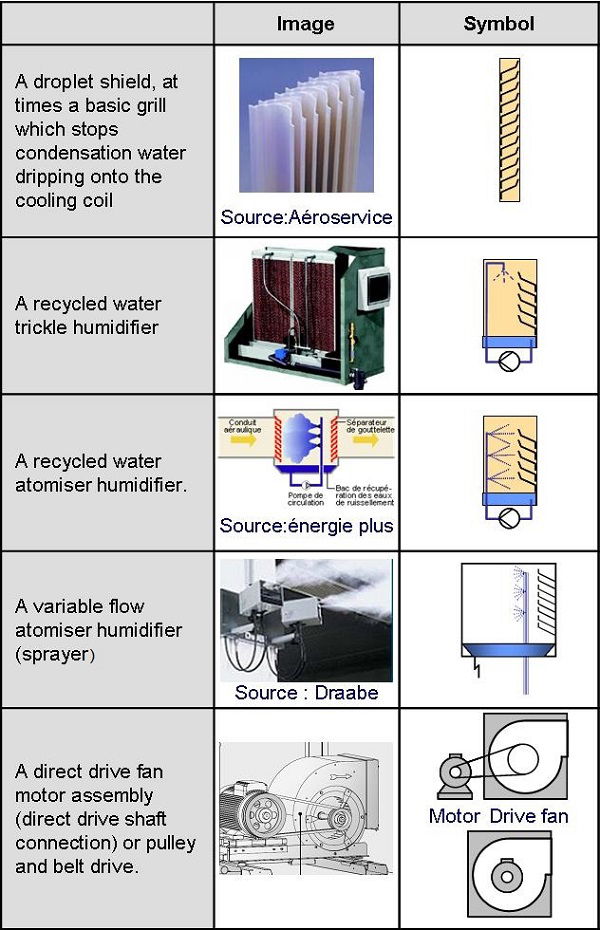
7: Droplet shield
8: Recycled water atomizer humidifier
9: Fan blower motor
10: Fan blower
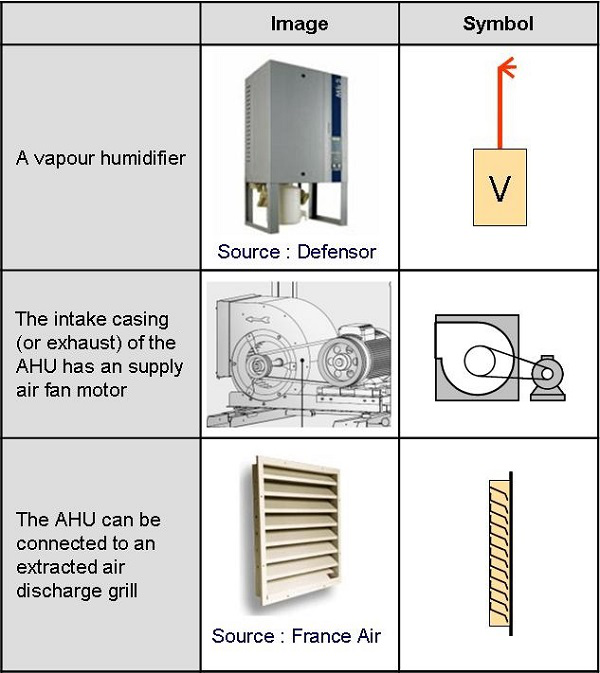
11: Vapor humidifier
12: Intake (or exhaust) fan motor assembly
13: Discharge grill
14: Blower box
15: Intake (or exhaust) box
16: Blower duct
17: Intake (or exhaust) duct
18: Discharge duct